
Make sure to provide the exact name of the AppImage file in the aforementioned command. Double-click on the AppImage file to launch Etcher.Īlternatively, you can also use the chmod command to assign executable permissions to the file.Go to the Permissions tab and tick the checkbox next to Allow executing file as program.Right-click on the AppImage file and select Properties.Extract the downloaded ZIP file to get the Etcher AppImage.Once downloaded, follow the steps below to get started: The easiest way to run Etcher on your Linux system is by downloading the AppImage file. 1. Run Etcher Directly Through the AppImage There are two ways to go about this: you can either download the Etcher AppImage from Balena's official website or install the software directly via the command line.
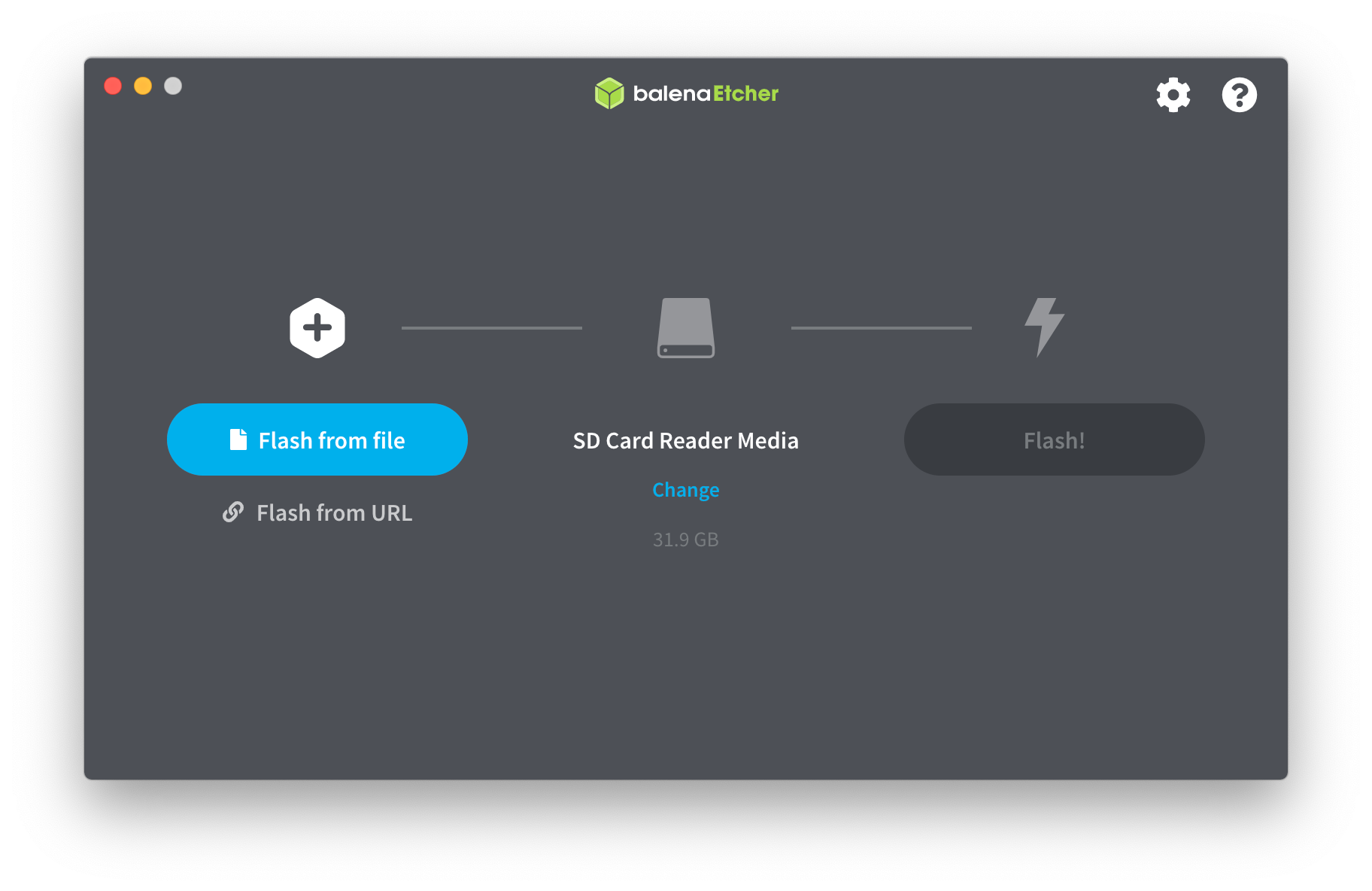
So if you accidentally plug in a defective SD card or flash drive, the software will notify you about the same, rather than flashing the image file onto the corrupted drive and leaving you wondering why your boot drive isn't working.īefore you start using Etcher, you first need to install it and set it up on your computer. One aspect of Etcher that separates it from some of the other image flashing utilities is its ability to validate the removable device before initiating the flashing process.

To create a bootable drive with it, all you need to do is perform a few simple steps, and it'll take care of flashing the image file onto your selected storage media. With Etcher, you get a pretty intuitive graphical user interface (GUI): one that's both easy to navigate and use. It's free to use and available across all major platforms: Linux, macOS, and Windows. What Is Etcher?Įtcher, also referred to as balenaEtcher, is a program used for writing image files onto storage devices, such as USB flash drives and SD cards.
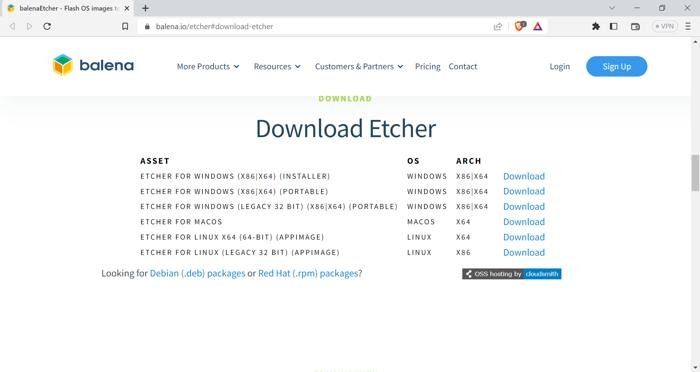
Here's a guide to help you through the process. If you're on Linux, you can use Etcher to create a bootable drive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
